Sugar beet vs sugar cane: Economic impact in the global sugar market
Everything About Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Which One Offers Greater Conveniences and Utilizes?
The contrast between sugar beet and sugar cane offers a nuanced exploration of their particular advantages and applications. Each plant has distinctive nutritional profiles and growing problems that affect their usage in various sectors. As consumer preferences change towards much healthier alternatives, the relevance of these 2 sources of sugar becomes significantly substantial. Recognizing their differences could reveal understandings into which might eventually offer much better in a changing market landscape. What elements will form this continuous dispute?
Overview of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 primary sources of sugar, each with distinctive qualities and advantages. Sugar beet, an origin plant largely grown in warm climates, is recognized for its high sucrose web content, which can vary from 15% to 20%. This crop is usually refined into granulated sugar, molasses, and other by-products. Its farming enables for a much shorter expanding period and much less dependence on tropical climates.
In contrast, sugar cane flourishes in warmer, tropical regions and is often pertained to for its fibrous stalks, which can generate 10% to 15% sucrose. The handling of sugar cane not just generates sugar yet additionally causes products like rum and ethanol, making it versatile. Both plants contribute significantly to the worldwide sugar market, with their special expanding conditions and processing techniques affecting their agricultural and economic value. Eventually, the option between sugar beet and sugar cane commonly depends upon regional climates and market needs.
Nutritional Profiles: Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane
The dietary accounts of sugar beet and sugar cane disclose considerable differences in their nutrient compositions. Sugar beet tends to supply a greater concentration of minerals and vitamins, while sugar cane mainly offers energy in the kind of carbs. Additionally, the glycemic index of these 2 resources varies, impacting their results on blood sugar level levels.
Nutrient Composition Contrast
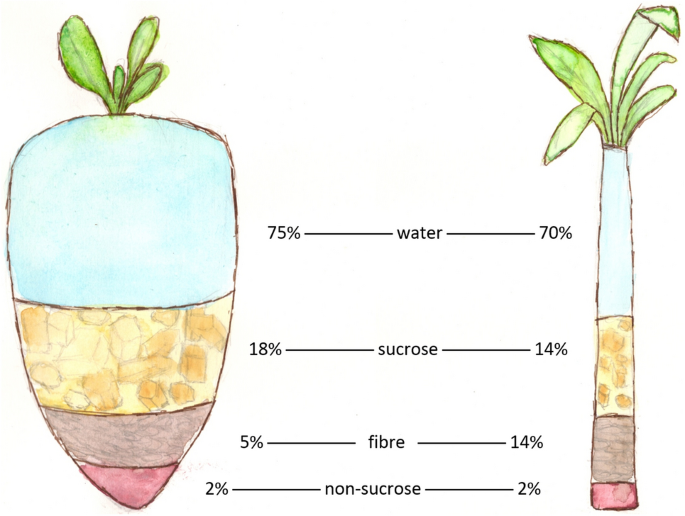
When contrasting the nutrient structure of sugar beet and sugar cane, distinct distinctions emerge that can affect dietary selections. Sugar beets are understood for their higher fiber web content, supplying approximately 2 grams of fiber per 100 grams, while sugar cane has marginal fiber (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Regarding vitamins, sugar beets use a variety of B vitamins, specifically folate, which sustains mobile wellness, whereas sugar cane includes less vitamins generally. Additionally, sugar beetroots boast a greater mineral content, including potassium and magnesium, vital for different bodily features. Sugar cane mainly supplies carbohydrates, specifically sucrose, but does not have the nutrient density found in sugar beets. These differences highlight the nutritional advantages of sugar beetroots compared to sugar cane in a well balanced diet

Glycemic Index Differences
Just how do sugar beetroots and sugar cane differ in their glycemic index, and what effects does this have for people monitoring their blood sugar level levels? Sugar beets generally have a reduced glycemic index (GI) compared to sugar cane, which suggests they create a slower and more progressive rise in blood glucose levels. This difference is especially important for individuals with diabetic issues or those worried about blood glucose monitoring. A reduced GI food can aid maintain steadier energy levels and reduce the risk of insulin spikes. While both sources are primarily composed of sucrose, the differing fiber and nutrient material in sugar beetroots may contribute to their reduced GI, making them a possibly far better option for health-conscious consumers.
Expanding Problems and Geographical Distribution
Both sugar beet and sugar cane serve as important sources of sugar, their growing conditions and geographic circulation vary greatly. Sugar cane thrives in tropical and subtropical environments, needing warm temperature levels, bountiful sunshine, and considerable rains. It is generally grown in nations such as Brazil, India, and China, where these environmental factors are perfect. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. In contrast, sugar beet favors pleasant environments, growing in cooler areas with well-drained soil. Major manufacturers of sugar beet consist of the USA, Russia, and numerous European countries, where the expanding period straightens with cooler temperature levels
The distinctions in climate requirements cause differing farming methods; sugar cane is frequently grown as a seasonal crop, while sugar beet is usually planted each year. This geographical difference not only influences regional farming economic situations however likewise shapes neighborhood methods associated to sugar production and handling. Recognizing these elements is important for evaluating the advantages and Website applications of each source.
Ecological Effect of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Production
While both sugar beet and sugar cane add considerably to global sugar manufacturing, their environmental influences differ considerably. Sugar cane growing frequently demands large stretches of land and water, resulting in logging and habitat loss in some areas. Furthermore, making use of plant foods and chemicals in sugar cane farming can result in dirt destruction and water pollution. Conversely, sugar beet is usually expanded in cooler environments and requires less water, which might lower the strain on regional water resources. Nevertheless, intensive farming methods related to sugar beet can also cause dirt erosion and nutrient exhaustion. The processing of both crops produces waste, but sugar cane has a greater potential for by-products, such as bioenergy, which can mitigate some environmental effects. Ultimately, the sustainability of each crop greatly depends upon farming techniques and local administration approaches utilized throughout the production cycle.
Handling Approaches and Efficiency
Processing techniques for sugar beet and sugar cane differ substantially, impacting general performance and return. Sugar beetroots undergo a process that includes washing, slicing, and drawing out juice with diffusion or pushing. The juice is after that cleansed, focused, and taken shape, causing granulated sugar. This approach is usually efficient, with a high sugar extraction rate.
On the other hand, sugar cane handling includes squashing the cane to essence juice, complied with by information and dissipation. The juice is after that boiled to create sugar crystals. While both techniques are reliable, sugar cane handling can be a lot more labor-intensive and lengthy because of the larger scale of operations and the need for much more comprehensive equipment.
Sugar beet handling usually results in a greater sugar content per bunch contrasted to sugar cane, making it link a much more effective option in particular areas. In general, the choice of handling method affects not just the yield however additionally the economic viability of sugar manufacturing.
Applications in the Food Market
In the food sector, sugar beet and sugar cane serve distinct functions in sweetener manufacturing. Each source supplies special qualities that affect their cooking applications, from baked goods to drinks. Understanding these distinctions can aid suppliers and chefs in picking the most suitable component for their demands.
Sweetener Manufacturing Differences
Although both sugar beet and sugar cane act as essential resources for sugar manufacturing, their applications in the food industry differ considerably. Sugar cane is mainly connected with generating raw sugar and molasses, which are commonly used in beverages, confections, and baked products. Its juice is also fermented to produce rum. Alternatively, sugar beet is primarily refined right into refined sugar, which is favored in the manufacturing of granulated sugar and various other sweeteners. The removal procedure for sugar beet is a lot more uncomplicated, permitting higher returns of white sugar. Additionally, sugar beet's versatility makes it possible for the creation of different sweeteners, such as beet syrup. These differences highlight the distinctive roles each source plays in fulfilling the diverse needs of the food market.
Culinary Makes Use Of Comparison
Cooking applications of sugar beet and sugar cane disclose distinctive preferences among chefs and food suppliers. Sugar cane, frequently perceived as the conventional sugar, is preferred in a selection of products, including syrups, molasses, and beverages like rum. Its natural flavor complements desserts, marinades, and sauces. Conversely, sugar beet, made use of mostly in granulated sugar kind, is regularly integrated into baked items, sweets, and processed foods. Its neutral flavor profile allows it to blend seamlessly into various dishes. In addition, sugar beet is obtaining grip in natural and non-GMO markets, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Eventually, the choice between sugar beet and sugar cane rests on specific cooking applications, taste preferences, and market patterns within the food market.
Health And Wellness Considerations and Consumer Preferences
An expanding number of customers are significantly mindful of the health and wellness ramifications related to sugar sources, click over here now resulting in a keen interest in the advantages of sugar beet versus sugar cane. Both sugar sources have distinct dietary profiles that may affect consumer options. Sugar beets tend to have somewhat much more fiber and necessary nutrients, which can attract health-conscious individuals. Alternatively, sugar cane is often regarded as a more all-natural and much less processed option, possibly drawing in those seeking natural or raw items.
In addition, the climbing appeal of alternate sweeteners has actually prompted customers to scrutinize typical sugars more carefully. Awareness of too much sugar consumption's health and wellness risks, such as weight problems and diabetes, has actually fueled a demand for openness concerning the beginnings and processing techniques of sugar. Inevitably, private choices continue to form the argument in between sugar beet and sugar cane, reflecting a more comprehensive trend towards much healthier eating routines and educated consumerism
Often Asked Concerns
What Are the Historical Uses of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
Historically, sugar beet and sugar cane have actually functioned as key sources of sugar. Sugar cane, cultivated for centuries in exotic areas, supplied sugar, while sugar beet arised in Europe throughout the 18th century, enhancing local sugar production.

How Do Sugar Beet and Cane Affect Local Economies?
Sugar beet and sugar cane considerably effect local economic situations via work production, farming performance, and profession. Their farming cultivates country growth, sustains regional companies, and generates tax revenue, inevitably enhancing community sustainability and financial durability.
Are There Any Type Of Cultural Relevance Differences In Between Sugar Beet and Cane?
Cultural importance varies between sugar beet and sugar cane. Sugar cane frequently stands for exotic heritage and standard methods, while sugar beet is related to farming technology and automation, showing different local identities and historical contexts in their manufacturing.
What Are the Key Pests Affecting Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The primary parasites affecting sugar beet include aphids and root maggots, while sugar cane encounters threats from borers and planthoppers. Both crops require mindful administration to minimize damage and warranty healthy returns.
How Do Environment Modifications Influence Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Cultivation?
Environment changes substantially affect sugar beet and sugar cane farming by altering growth conditions, moving pest populations, and impacting water availability. These elements can lower yields and impact total agricultural sustainability in impacted areas.